How To Reduce The Effects Of Caffeine On Your Unborn Baby
If you drink more than 200 mg of caffeine per day during pregnancy, its best to cut back but remember that even if you do this, caffeine may still have a negative effect on your baby.
Caffeine is in many beverages and products you can buy. You probably wont be able to cut out all caffeine from your diet completely. But thats okay because the daily limit of 200 mg is an average amount not a precise limit for everyone. If you drink 2 cups of coffee, you probably dont need to cut back to 1 cup if you drink only ½ cup, you may not need to cut back at all.
Some common sources of caffeine in addition to coffee and tea are:
Energy drinks
Soft drinks
Chocolate, particularly dark or bakers chocolate
Caffeine in coffee, tea, soda etc., one serving of each is about equivalent to the other caffeinated beverages. For example, if you drink a cup of coffee or tea with 150 mg of caffeine, youd need to drink 8.5 cans of soda or 5-6 cups of brewed cocoa to get the same amount of caffeine.
Caffeine can be found in many sources of beverages and products, so it may not be possible to eliminate all caffeine from your diet. However, by limiting your intake to no more than 200mg per day you will avoid some negative effects such as an increased risk for miscarriage or premature birth and hyperactivity disorders in children. Be sure to speak with a physician before changing anything about what you eat or drink during pregnancy!
Interindividual Variation In Caffeine Response
Notably, caffeines effects on pregnancy outcomes have been shown to be highly variable between individuals in both rodents and humans . Substantial interindividual phenotypic variation and the underling mechanism in complex traits and diseases have become an area of significant scientific interest over the past two decades. It is now increasingly accepted that an individuals disease susceptibility is a complex readout of combined effects from genetic, epigenetic, and environmental inputs as well as their dynamic interaction during the process of development . However, the relative weights of these different factors in the contribution of interindividual variation and disease predisposition varies case by case and depends on specific conditions and sometimes may show significant synergism.
Interindividual Variability in Caffeine Response.
Postulated models underpinning the highly variable individual response to caffeine exposure. Women showed different responses to caffeine exposure during pregnancy . The effects of caffeine might be regulated by multiple factors in vivo, including the ability to metabolize caffeine and cellular targets , or regulated through modulators associated with pregnancy and fetal development, all of which modify the outcome of pregnancy for individual women after caffeine exposure. Abbreviations: ADORA1, adenosine A1 receptor ADORA2A, adenosine A2A receptor CYP1A2, cytochrome P450 1A2.
Effects Of Maternal Caffeine And Vitamin E Usage On Fetus
1Department of Anatomy, Yozgat Bozok University Faculty of Medicine, Yozgat, Turkey
2 Tekirda Namik Kemal University, Faculty of Medicine, Tekirda, Turkey
3 Department of Medical biology, Faculty of Medicine, Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University, Afyonkarahisar, Turkey.
4 Department of Anatomy, Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey
5 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Yozgat Bozok University, Yozgat, Turkey
*Corresponding Author: Adem Tokpnar, Tekirda Namik Kemal University, Faculty of Medicine, Tekirda, Turkey
Citation: Ylmaz S., Tokpnar A., Ate S., Köklü B., Evrim S. Arkan, Uçar S. , Aye Yeim G. Effects of Maternal Caffeine and Vitamin E Usage on Fetus. J. Obstetrics Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences 6 DOI: 10.31579/2578-8965/109
Copyright: © 2022, Adem Tokpnar, This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received:01 December 2021 | Accepted:18 December 2021 | 11 January 2022
Keywords: rat pregnancy ossification caffeine oxidative stress
Abstract
The use of maternal caffeine has an important effect on the development of the fetus. We investigated the mechanism of oxidative damage induced by caffeine and the efficacy of vitamin E.
Introduction
Material and Methods
Selection and Mating of Experimental Animals
Preparation of Injections
Results
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Coffee For Your Health
Subgroup Sensitivity Analyses And Publication Bias
Regarding the significant positive association between caffeine intake and the risk of pregnancy loss, findings from the sensitivity analyses indicated that this association was dependent on particular studies. For example, exclusion of studies by Gaskins et al. , Wen et al., Giannelli et al., and Maconochie et al. resulted in a non-significant association between caffeine intake and pregnancy loss. When we excluded the study by Savitz et al., pooled effect estimates resulted in a significant association .
Findings from another sensitivity analysis revealed that excluding any single study from the analysis did not appreciably alter the pooled effect sizes . No publication bias was found based on Eggers regression asymmetry test . In terms of caffeine intake during pregnancy and pregnancy loss, Eggers linear regression test indicated some degree of publication bias however, the trim and fill methods application did not change the average effect size, further suggesting that results were not affected by publication bias. Three missing studies were imputed in regions of the contour-enhanced funnel plots to adjust for asymmetry .
Caffeine And Fetal Growth
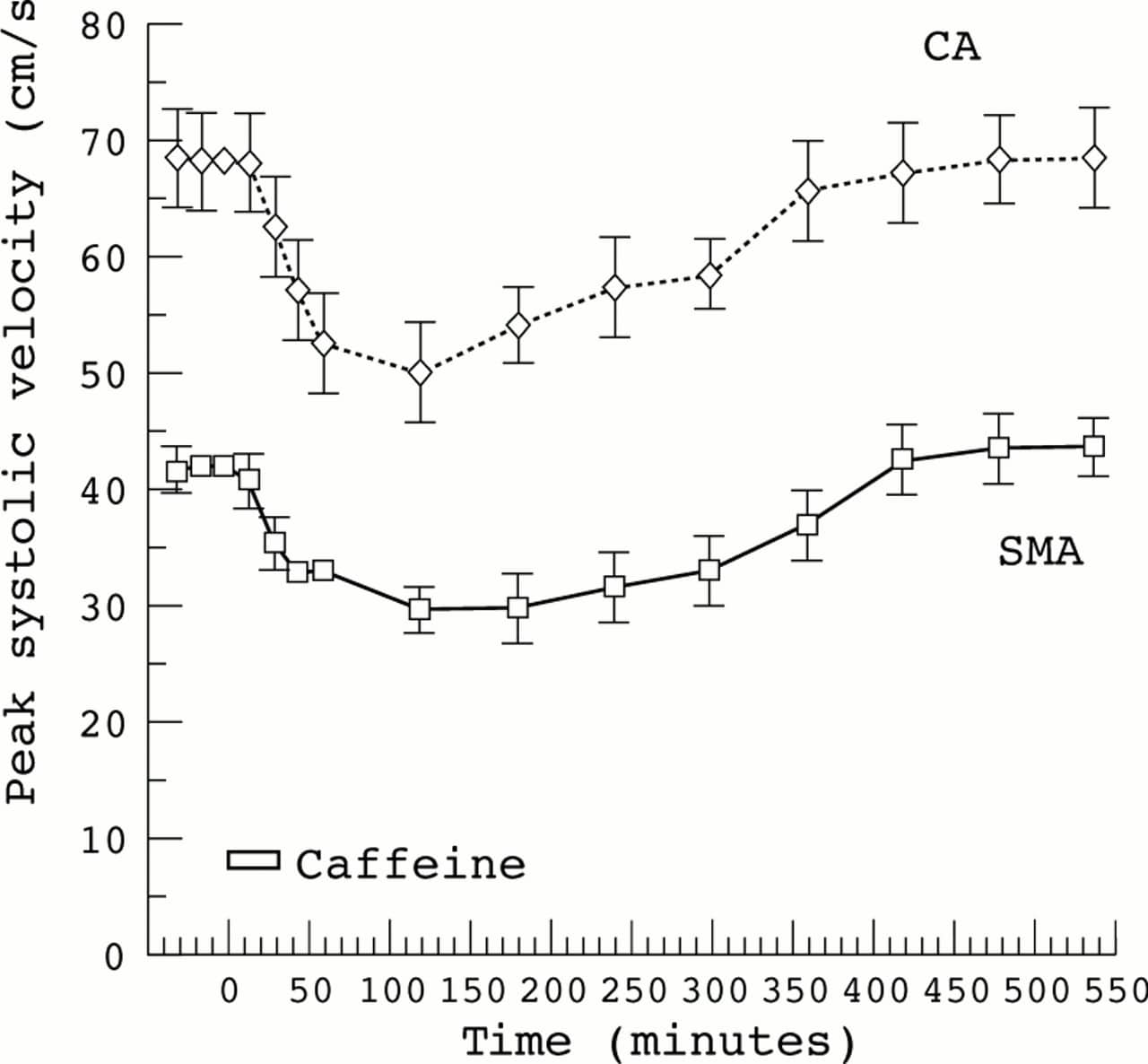
Studies of caffeine and fetal growth restriction are equivocal. Some studies showed no effects on growth, whilst others demonstrated a risk of growth retardation with increased exposure to caffeine, although with the inability to determine the role of confounding factors1,13.
One of the larger studies was the Dutch Generation R Study, a prospective cohort study which included 7,346 pregnant women. Inconsistent associations were observed between caffeine intake and fetal head circumference, or estimated fetal weight. Higher caffeine intake was associated with shorter birth length, suggesting that fetal growth may be impaired by caffeine35. However, further studies are needed to assess these associations in non-European populations and the possible postnatal consequences of the observed fetal growth restriction. Results from a large prospective cohort in which the main caffeine source was coffee, showed that coffee but not caffeine, was associated with marginally increased gestational length but not with spontaneous preterm delivery29. However, caffeine intake was consistently associated with decreased birth weight and increased odds of the baby being small for its gestational age29.
The 2010 Committee Opinion of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists stated that the relationship between caffeine and growth restriction remains undetermined34.
Read Also: Kiser Cappuccino 2-piece Sectional
The Effects Of Caffeine On The Baby Of A Pregnant Mother
Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, soft drinks, chocolate, frozen desserts, gum and some over-the-counter drugs. According to the Mayo Clinic, consuming more than 500 mg of caffeine a day can lead to insomnia, nervousness, restlessness, irritability, nausea or other gastrointestinal problems, fast/irregular heartbeat, muscle tremors, headaches and anxiety in adults. The chemical can also have lasting effects on babies developing in the womb.
How Much Caffeine Is Too Much
Many experts say that the less caffeine you consume, the better. Others say more than 150 mg of caffeine a day is too much, while others say more than 300 mg a day is excessive. Avoiding caffeine as much as possible is your safest course of action. If you cant resist caffeine, it is best to discuss details with your healthcare provider.
Want to Know More?
You May Like: Will Caffeine Raise Blood Sugar
Potential Link To Leukemia Risk
No convincing links have been found between caffeine and cancer risks, but a study announced on January 2009 on ScienceDaily.com is rooted in the findings of previous research that did find a correlation between alterations to DNA, sometimes found in newborns, to an increased risk of leukemia. Caffeine has been known to trigger these types of DNA changes. Lifestyle and dietary information will also be considered to determine if other factors could also increase the risk. Past research suggesting a link between caffeine with cancers of the pancreas and kidneys found that the stimulants effect on cancer risk was unlikely.
- No convincing links have been found between caffeine and cancer risks, but a study announced on January 2009 on ScienceDaily.com is rooted in the findings of previous research that did find a correlation between alterations to DNA, sometimes found in newborns, to an increased risk of leukemia.
Can Pregnant Women Drink Coffee
The short answer is yes, pregnant women can drink coffee. However, it’s important to watch your consumption of coffee, and caffeine overall, during pregnancy. Caffeine can affect your pregnancy and your baby in ways that aren’t completely clear.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists advises pregnant women to limit their caffeine intake to less than 200 milligrams per day, which could be as little as one 8-ounce cup of coffee, depending on the brand. See the chart below to get an idea of how much caffeine is in different foods and drinks.
Read Also: Is There Caffeine In Dr Pepper Zero
+ Fertility Smoothie Ingredient #7 Prebiotic + Probiotic
As mentioned above under #5, when gut bacteria becomes unbalanced our food and nutrients arent absorbed as well, and larger molecules are able to cross the gut wall, causing food sensitivities and increasing inflammation in the body.
Thus, incorporating foods that both feed the good bugs in your gut as well as those that help strains of good gut bacteria flourish are key for a balanced gut microbiome, equating to a healthier gut and healthier hormones.
A few of my favorite prebiotic-rich foods to add to smoothies include bananas, plantains and apples, while full-fat coconut or greek yogurt and kefir are complementary probiotic sources.
Effects Of Caffeine During Pregnancy
When you drink a cup of coffee, caffeine crosses the placenta into the amniotic fluid and your baby’s bloodstream. While your body goes to work metabolizing and getting rid of the caffeine, your baby’s body is still developing and takes a much longer time to process the caffeine. As a result, your baby is exposed to the effects of caffeine for much longer than you are.
Even if caffeine doesn’t usually cause problems for you, you may find that it doesn’t agree with you during pregnancy. It’s a stimulant, so it can raise your heart rate and blood pressure. Plus, it can make you feel jittery and cause insomnia. Caffeine can exacerbate pregnancy issues like heartburn and frequent urination, too.
The effects of caffeine may be more noticeable as your pregnancy progresses. That’s because your body’s ability to break down caffeine slows, so you end up with a higher level of it in your bloodstream. During the second trimester, it takes almost twice as long to clear caffeine from your body as when you’re not pregnant. During the third trimester, it takes nearly three times as long. This can also mean that more caffeine crosses the placenta and reaches your baby, who can’t process it efficiently.
Wondering when you can get back to enjoying your regular caffeine habit? It depends. Some caffeine can cross to your baby in breast milk, which is why it’s also a good idea to limit caffeine if you’re breastfeeding, especially for the first few months.
Also Check: How Much Caffeine Snapple Peach Tea
Is Any Amount Of Coffee Safe For Baby During Pregnancy
HealthDay Reporter
FRIDAY, Feb. 12, 2021 — Too much coffee during pregnancy could lead to kids with behavior problems later on.
That’s the key takeaway from new research that examined 9,000 brain scans from 9- and 10-year-olds as part of the largest long-term study of brain development and child health.
“The goalposts are moved by caffeine, and there are subtle, but real changes in behavioral outcomes in most kids who were exposed to caffeine in utero,” said study author John Foxe. He is director of the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester in Rochester, N.Y.
“This may not make a meaningful difference in the behaviors of some kids, but for those who are vulnerable in other ways, it may flip them over the threshold,” Foxe added.
For years, pregnant women have been told to limit their caffeine intake to lower their risk for miscarriage or preterm birth, but this new study suggests that pregnant women who consume any coffee may be more likely to have kids with behavioral issues later in life.
Brain scans of kids whose mothers consumed caffeine during pregnancy showed changes in pathways that could lead to behavioral problems later on, including attention difficulties and hyperactivity. The changes tracked with higher scores on checklists for problem behaviors seen among kids whose moms reported drinking coffee while pregnant.
The study did not find any changes in the children’s intelligence or thinking ability.
More information
Show Sources
Caffeine Levels In Common Drinks And Snacks

- Coffee, average :
- Brewed, 8 oz. | 95 165 mg
- Brewed, decaf, 8 oz. | 2 5 mg
- Espresso, 1 oz. | 47 64 mg
- Latte, 8 oz. | 63 126 mg
Don’t Miss: How To Buy Coffee Stocks
Drinking Coffee While Pregnant
Instead, the study authors used a method called Mendelian randomization to look at genetic variations caused by caffeine consumption during pregnancy. Study author Dr. Gunn-Helen Moen explained to Medical News Today:
We used genetic analyses to mimic a randomized control trial, using eight genetic variants associated with coffee consumption that predict coffee-drinking behavior.
Dr. Brian Power, a clinical dietitian and academic who was not involved in the study, also noted how helpful this method is:
The study team used a genetic approach called Mendelian randomization, which uses naturally occurring genetic differences to simulate the effects of a clinical trial, to test causal effects of caffeine on pregnancy outcomes. Using this robust genetic analysis among a large population helps to remove bias from the results.
Researchers wanted to find out if caffeine consumption causes specific poor pregnancy outcomes. They specifically examined the relationship between coffee consumption during pregnancy and the following:
- pre-term birth and gestational age
The methods they used helped to separate the caffeine intake from other factors.
Results of the study suggested that coffee likely does not contribute to miscarriages, stillbirths, lower gestationalage, or pre-term birth.
However, the findings regarding birth weight suggested that coffee consumption might be associated with higher birth weight. But authors note that the magnitude of the effect was inconsistent.
Why Food Matters For Fertility
A key component of optimal fertility is obtaining enough nutrients from the food we eat. This is because nutrients are absolutely essential for hormone production. Without them, our hormones cannot do their jobs effectively, which can lead to fertility challenges, typically in the form of irregular ovulation or a shortened luteal phase .
Nutrients arent only necessary for a healthy cycle and conception, but for a healthy egg, pregnancy and baby as well . In fact, researchers from the Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of the Columbia University Medical Center believe the preconception period to be just as crucial to both mom and babys health as what happens once the fetus is in utero.
Because the quality of both the egg and the sperm begin developing 90 days prior to conception, its never too early to begin incorporating fertility-boosting foods into your diet, especially if thats the direction you know you are heading.
Don’t Miss: Wawa French Vanilla Cappuccino Caffeine
How Much Caffeine Is Safe During Pregnancy
Although the official recommendation is 200 mg or less a day, some experts believe that even moderate amounts of caffeine during pregnancy can introduce risks.
Previously, studies have linked high caffeine consumption to babies being small for their gestational age or at risk for intrauterine growth restriction . But researchers at the National Institutes of Health recently found that women who drank less than 200 mg of caffeine a day during pregnancy as little as half a cup of coffee per day had slightly smaller babies than non-caffeine drinkers.
Researchers noted that caffeine is believed to cause blood vessels in the uterus and placenta to constrict, which could reduce the blood supply to the fetus and inhibit growth. They also said that caffeine could potentially disrupt fetal stress hormones, putting infants at risk for rapid weight gain after birth and for obesity, heart disease and diabetes later in life.
However, other studies have found no link between moderate caffeine consumption in pregnancy and problems such as low birth weight, IUGR, miscarriage, or premature birth. That’s why moderate caffeine consumption during pregnancy gets the okay from most ob-gyns and midwives.
Still, because the research isn’t settled, it’s a good idea to limit your caffeine consumption as much as possible during pregnancy, and to stay within the recommended 200-mg-a-day limit.
Why The Concern Over Smaller Stature
If shorter height in early childhood were to persist into adulthood, there would be a chance those children could face the risk of poor cardiometabolic outcomes, such as heart disease and diabetes, which are associated with smaller stature.
But there is still no way to know if the difference would persist into adulthood, and studies like this that focus on population outcomes are no reason for individual families to panic, Gleason said.
These population-level trends should instead be taken together with other research for organizations to reassess their recommendations, Gleason said.
In the past, there were inconsistent studies regarding whether consuming caffeine during pregnancy impacted the fetus, but the evidence has come together in recent years, Gleason said.
A 2015 meta-analysis that reviewed all of the existing research found there is a dose response association between consumption of caffeine and smaller birth size. And a 2020 study revealed there is no safe level of caffeine for a developing fetus.
Don’t Miss: Does Walmart Sell Keurig Coffee Makers