Caffeine And Cardiovascular Health: What You Need To Know
Filed under: General, News · February 6th, 2020
The month of March is full of fun holidays and silly national days like St. Patricks Day, National Oreo Cookie Day and National Napping Day. But one important holiday that is often overlooked actually spans the whole month of MarchCaffeine Awareness. According to the FDA, 80% of adults in the United States consume some form of caffeine every day. This can include anything from your typical cup of coffee to tea, supplements or soda. To put it lightly, Americans are so obsessed with their caffeine that weve dedicated a whole month of awareness to this natural stimulant! The heart experts at AMS Cardiology are here to share everything you need to know about caffeine and your cardiovascular health to sip safely this month.
Where Is Caffeine Found?
Caffeine naturally occurs in roughly 60 plant species, with the most well-known being coffee beans, tea leaves and cocoa beans. You can see it in the form of guarana, found in many popular energy drinks and yerba mate in teas that are popular in South America. Not only found in beverages, you can also find caffeine in many packaged foods as well as dietary supplements.
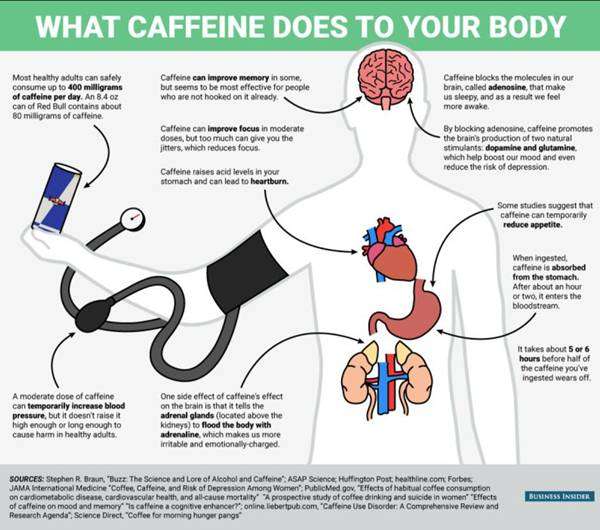
Caffeine and Heart Health
Home Much Is Too Much?
How to Cut Back on Caffeine
Coffee And Your Heart: Stimulant Or Stressor
The latest research suggests drinking your morning cup is safe for your heart, and may even be good for it.
Danijela Froki/Unsplash
Drinking coffee was once lumped in with smoking, heavy drinking, and a couch potato lifestyle as a recipe for heart attack. Now, an abundance of evidence is painting the morning brew in a more favorable light. Most of us, even those with a history of heart disease, probably dont need to give up our daily mug or two.
Over the years, theres been a lot of misinformation and some misconceptions about coffee that all coffee is bad and that people shouldnt be drinking it, says Christine Jellis, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio. But recent studies with thousands of participants are turning those misconceptions around, and results have been reassuring for coffee lovers.
Mild to moderate consumption of coffee is probably doing us no harm, and theres actually some evidence to show that it might be doing us some benefit, says Dr. Jellis.
RELATED: The United States of Stress
You May Decrease Your Risk Of Getting Alzheimer’s Disease
Almost two-thirds of Americans living with Alzheimers disease are women. But the caffeine in two cups of coffee may provide significantprotection against developing the condition. In fact, researchers foundthat women age 65 and older who drank two to three cups of coffee a daywere less likely to develop dementia in general.
You May Like: Is There Caffeine In Snapple
Could Your Racing Heart Be Caused By Caffeine
It is not uncommon to hear patients say that, when they started experiencing racing or skipping a heartbeat, they stopped drinking caffeinated beverages. In general, there is a widespread perception that caffeine may be a root cause of a racing heart, even in light of our overwhelming consumption of caffeinated products, including energy drinks, coffee, and energy supplements.
Caffeine is a natural product that is derived from the raw fruit that grows on coffee plants. Some tea leaves also have caffeine, as does cocoa, kola nuts, and yerba maté. When we consume caffeine, the chemical is absorbed by the body within 30 minutes to an hour.
Could Caffeine Be Good For Your Heart
Studies suggest regular coffee use protects patients from atrial fibrillation.
Could caffeine be good for your heart?
How do you take your caffeine? Caffeine is a stimulant that has been linked to improving how your brain functions. No wonder it is one of the most widely used drugs on the planet. The most common forms of caffeinated beverages include coffee, tea and energy drinks. New research in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology suggests that caffeine is not harmful to the heart, as it has previously been suggested, and may actually be good for it.
Caffeine works by adding more energy to the inside of your cells. Because caffeine is known to make the heart beat faster, many people believe that it can be damaging to the hearts electrical system. In fact, greater than 80 percent of doctors in the U.S. recommend against caffeine consumption in patients with known abnormal heart rhythms. Many feel the faster heart rate makes your heart more vulnerable to entry into life-threatening rhythms.
On the other hand, caffeine has also been described as an antioxidant. Antioxidants neutralize the negative waste products of your cells day-to-day activities and are believed to preserve the long-term health of your cells and tissues. Some scientists believe that caffeine protects the longevity of the heart muscle itself.
So heres the good news.
Laura Shopp, MD, a third-year pediatrics resident affiliated with Indiana University, works in the ABC News Medical Unit.
You May Like: Starbucks Decaf House Blend Caffeine Content
Coffee Caffeine And Your Heart: Q& a With Dr Arrash Fard
Dr. Arrash Fard is here to answer all our questions about coffee and caffeine consumption, particularly for people with heart conditions like hypertension or heart disease.
Q: In general, there’s a lot of conflicting information out there about how coffee affects the heart . What’s your advice for those who either have a condition like heart disease or hypertension, or are at risk for developing one later in life, when it comes to interpreting all the contradictory research out there about coffee and heart health?
A: There is no strong evidence that coffee consumption has deleterious effects on heart health when consumed in modest amounts. To go further, medical literature does not support concerns of modest coffee intake on cardiac outcomes such as death or stroke. It is generally accepted as safe for most healthy adults to consume less than 400 mg of caffeine daily. It is generally not recommended for people to discontinue coffee or caffeine intake to try improving cardiovascular outcomes.
Q: Coffee aside, what should people with chronic heart-related conditions/people who are at risk of these conditions know about general caffeine use? Are there more risks/benefits associated with different forms of caffeine ?
Potential Negative Effects Of Caffeine
In contrast to the possible health benefits of caffeine, it does have some negative effects on the cardiovascular system especially when very large amounts of it are consumed daily. Caffeine can raise your heart rate and cause palpitations and extra heartbeats. And using large amounts of it for long periods can increase your risk of having a heart attack. This is particularly true in people who have diabetes.
Blood pressure can go up significantly after caffeine use because it seems to block a hormone our bodies produce to keep our arteries open wide. When caffeine makes the blood vessels in our bodies narrower, this leaves less room for blood flow which, in turn, raises blood pressure. The blood vessels supplying blood to the brain can also narrow as much as 27% after caffeine intake which can slow down our ability to think and perform mental tasks.
Coffee drinking is also linked to higher levels of cholesterol, especially in people who drink coffee that is processed at very high temperatures like espresso. And finally, caffeine has been shown to make arteries stiff which contributes to coronary artery disease or hardening of the arteries as we age.
Don’t Miss: Where Can You Buy Verismo Coffee Pods
How Do My Genetics Affect Caffeine And Blood Pressure
Genetics may account for up to 50% of differences in blood pressure . There is one gene specifically responsible for metabolizing caffeine called CYP1A2. Depending on your version of it, you are either good to go or youd better be careful.
The CYP1A2 rs762551 C variant is what is called the slow-metabolizing variant. If you are stuck with this, your body metabolizes caffeine slower than normal. Your risk of hypertension is higher if you consume caffeine .
If, on the other hand, you have one of the A variants, or what is known as the fast-metabolizing version, your risk of hypertension may actually be lower . Good news! Caffeine may actually protect you from hypertension!
Now, we wont say this justifies hitting up the coffee shop every morning in the name of good health, but at least you can strike that worry off the list.
What Happens To The Heart When You Consume Caffeine
Once you take that first sip of coffee, the caffeine enters your blood from the stomach and small intestine and begins to stimulate your central nervous system. The receptors in the cells within your heart are stimulated by the caffeine and increases your heart rate.
As your heart beats faster accelerating by about three beats per minute your blood flow speeds up, too. The increase in your heart rate from caffeine can take effect in as soon as 15 minutes and take approximately six hours to wear off.
You May Like: Undertow Starbucks Recipe
How Long Symptoms Last
According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, caffeines half-life is up to 5 hours. Half-life is the amount of time it takes for a quantity of a substance to be reduced to half the original amount.
So if youve consumed 10 milligrams of caffeine, after 5 hours, youll still have 5 mg of caffeine in your body.
The effects from caffeine reach peak levels within 30 to 60 minutes of consumption. This is the time youre most likely to experience the jittery effects of caffeine.
You might also urinate more due to the liquid volume being ingested and caffeines mild diuretic effect.
The other half of caffeine that you consume can last much longer than 5 hours.
People with caffeine sensitivities might feel symptoms for several hours or even a few days after consumption.
Due to the long-term effects of caffeine, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends that you dont consume it at least six hours before bedtime. So if you go to bed at 10:00 p.m., you should have your last round of caffeine no later than 4:00 p.m.
Does Caffeine Raise Blood Pressure
To be clear, caffeine does actually affect blood pressure. When you consume caffeine, whether it be from coffee, an energy drink, or supplement, one of its effects is to spike your blood pressure.
Caffeine raises blood pressure by blocking adenosine, a compound that helps blood vessels stay relaxed and open. Without the adenosine, blood vessels constrict, the heart must work harder to move blood through your system, and so the pressure rises.
This rise kicks off within 15 minutes of consumption and can last 4-6 hours. If you dont consume more, things should return to normal.
Many of us are in this position. We like our coffee or energy drink or soda or tea, and we pay no thought to the consequences of that little burst of blood pressure. Why? Because we never notice.
Hypertension, as stated above, has many risk factors, so you might get it irrespective of your caffeine consumption. If you get hypertension though, that spike in blood pressure can be serious, and caffeine will be one of the first things off the list if you get diagnosed with it.
For a small subset of us, our genetics make this all better or worse, depending on one little gene variant.
Recommended Reading: Does The Dragon Drink Have Caffeine
Caffeine In Individuals At Rest Improves Ecf
Caffeine in individuals at rest is believed to improve ECF by increasingintracellular calcium, which in turn stimulates expression ofendothelial nitric oxide synthase, which itself stimulates theendothelial cells to produce nitric oxide. The nitric oxide thendiffuses to the vascular smooth muscle, which lies just underneath theendothelial cells, and results in vascular smooth muscle vasodilatation. Caffeine can also bind directly to the vascular smoothmuscle cell receptors and, through similar mechanisms, causevasodilatation .
Caffeine Plus Exercise Decreases Ecf

As a sports cardiologist, Higgins is especially interested in ECF asmeasured by myocardial blood flow. He described results from threestudies based on measurements of either myocardial perfusion by positronemission tomography or brachial artery ECF by flow-mediated dilation. Flow-mediated dilation measurements are also anaccepted surrogate for coronary artery ECF .
Also Check: Is There Caffeine In Snapple
How Much Coffee Is Safe For Women To Drink Each Day
Its true, you can have too much of a good thing. Excessive intake ofcaffeinated coffee can make you jittery and cause:
- Increased heart rate
- Anxiety
- Trouble falling asleep
So how much coffee is the optimal amount to drink to get all the benefits,but avoid the negative side effects?
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, its safe for most womento drink three to five cups of coffee a day with a maximum intake of 400milligrams of caffeine.
But if youre pregnant or breastfeeding, the rules are different. Checkwith your obstetrician before adding caffeine into your diet.
Vizthum also cautions, Caffeine tolerance is different for everyone. Youwant to do what makes you feel good. You can still get some of thepotential health benefits by drinking one cup of coffee a day, or even bydrinking decaffeinated coffee.
Also, remember that what you add to your coffee can make a difference inhow healthy the beverage really is. Instead of loading up on cream andsugar, Vizthum suggests adding up to two tablespoons of milk, milksubstitute or half- and- half, and using naturally sweet spices andflavorings. Try stirring in a ¼ teaspoon of the following for extra flavor:
- Vanilla extract
- Cinnamon
- Cocoa powder
What The Latest Science Says About Caffeine’s Influence On Your Heart Memory Sex Life And Exercise Performance
Americans are jolted with caffeine. On average, about 80% of adults take some form of caffeine every day, according to the FDA, usually from coffee, tea, soda, or energy drinks.
But does all that caffeine have any effect on your health either good or bad? “While caffeine can give you a temporary mental and physical boost, its impact depends on how much you consume and the source,” says Dr. Stephen Juraschek, an internal medicine specialist at Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctor’s visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
Also Check: Do K Cups Work In Verismo
Caffeine And Your Heart
Caffeine is one of the most researched dietary components, and we know a lot about how it affects the body. However, research examining caffeines link to heart palpitations has been conflicting, with some studies showing a connection and others not.
This is because in healthy people, caffeine does not appear to cause heart palpitations. However, some people may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine and may experience heart symptoms such as palpitations.
Caffeine affects the heart in multiple ways. Firstly, it promotes the release of noradrenaline and norepinephrine. Among other things, these hormones increase heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, caffeine can act on enzymes that stimulate heart contractions, causing the heart to contract with more force.
Caffeine And Your Blood Pressure
Studies investigating the effect of coffee on blood pressure have yielded varied results. In general, caffeinated coffee causes a short-term spike in blood pressure in people who dont drink it regularly. This is because caffeine stimulates the heart and blood vessels, according to the Mayo Clinic. In a 12-year study of more than 1,000 people ages 18 to 45 who had high blood pressure, those who drank four or more cups of coffee per day were four times more likely to have a heart attack or stroke. In contrast, long-term studies have shown that most people develop a tolerance to caffeine over time. Reviews of numerous studies show coffee drinkers were no more likely to develop hypertension than abstainers, and those who already had high blood pressure were no more likely to develop cardiovascular disease.
Some people are more sensitive to caffeine-induced stress than others, and evidence suggests genetic differences are at play. In a study of more than 2,000 heart attack cases published in The Journal of the American Medical Association, people who were slower to metabolize caffeine because of their genes were found to be more likely to have heart attacks.
RELATED: 9 Healthy Reasons to Indulge Your Coffee Cravings
I do think there may be a small subgroup of people with hypertension in whom caffeine should be restricted, says Dr. Estes, emphasizing the need for individualized recommendations.
Recommended Reading: Can I Have Coffee After Wisdom Teeth Removal
What Is It About Coffee That Affects Your Heart
Coffees heart-health perks may be related to naturally-occurring compounds in coffee beans other than caffeine. Coffee contains hundreds of unique phytochemicals that may help reduce inflammation, which is good news for your heart, says Jellis, because, “Theres thought to be an inflammatory component underlying some causes of heart failure, atherosclerosis, and other conditions, so the anti-inflammatory properties of coffee compounds may be contributing to the perceived long-term benefits in terms of cardiovascular disease.”
But if youre anxiety-prone, even drinking coffee in moderation may not be healthy for you. If individual patients feel theyre having cardiovascular symptoms that are worsened with coffee most commonly palpitations or feelings of being anxious the common-sense advice is to go decaf, says N. A. Mark Estes, MD, director of the New England Cardiac Arrhythmia Center at Tufts Medical Center in Boston.
Music Creation Resources And Tools
For aspiring producers, songwriters and composers, there has never been a time where this much information about music creation and theory has been right at our fingertips. There are so many digital tools available to both make and learn music that almost anyone with an interest can pick them up and start making sounds! Understanding how music works, however, is complex and that’s where online resources and tools such as blogs come in handy. You can use these tools to discover useful information such as the difference between rhythm and beat or how to compose a melody to further your understanding of music and how it’s made.
Also Check: Where To Buy Verismo Coffee Pods