What Does It Mean To Be A Fair Trade Company
Cafe Campesino has been a member of the Fair Trade Federation since 1999 and abides by the Fair Trade Federations nine principles:
Fair Trade Vs Direct Trade Coffee: The Jargon Of Sustainability
Just so you know, if you click on a product on RoastyCoffee.com and decide to buy it, we may earn a small commission.
These terms are thrown around a lot in just about every kind of coffee circle, from professional connoisseurs to casual drinkers. But what is the really difference between these two sustainability terms? And what do they mean about your coffee?
We are here to break down everything you need to know about fair trade and direct trade. Read on to find out what they mean to farmers, roasters, and your coffee.
What Does ‘fair Trade’ Actually Mean
You’ve likely heard the phrase and even seen the iconic blue and green logo on products such as chocolate, bananas, or coffee but do you know what it means?
If you’re a particular fan of chocolate , then you may have become familiar with the green and blue logo that frequently marks fair trade products. You’ve also likely come to expect that any commodity bearing that symbol is going to cost a bigger percentage of your grocery budget. But what exactly does it mean for your morning cup o’ Joe to be fair trade? And who benefits from that arrangement?;
To answer those questions, we’ve put together a brief guide explaining all the basics of the fair trade system. So if you’d like to better understand the meaning behind the sticker on your produce, feel free to follow along.
You May Like: Is There Caffeine In Snapple
The Problem With Fair Trade Coffee
Fair Trade-certified coffee is growing in consumer familiarity and sales, but strict certification requirements are resulting in uneven economic advantages for coffee growers and lower quality coffee for consumers. By failing to address these problems, industry confidence in Fair Trade coffee is slipping.
Peter Giuliano is in many ways the model of a Fair Trade coffee advocate. He began his career as a humble barista, worked his way up the ladder, and in 1995 co-founded Counter Culture Coffee, a wholesale roasting and coffee education enterprise in Durham, N.C. In his role as the green coffee buyer, Giuliano has developed close working relationships with farmers throughout the coffee-growing world, traveling extensively to Latin America, Indonesia, and Africa. He has been active for more than a decade in the Specialty Coffee Association of America, the worlds largest coffee trade association, and currently serves as its president.
Fair Trade Coffee Beans

Fairtrade has become a household word and many consumers love to support the concept of Fair trade but what does it really mean?
Fair trade as a definition is ‘trade between companies in developed countries and producers in developing countries in which fair prices are paid to the producers.’ . By definition, this makes all the coffee we sell Fair Trade. Our focus has always been to support ethical trade. This is done directly between us and the producer and some is done through the help of specialist coffee importers.;
Generally speaking, when discussing Fairtrade, most people are referring to the very well know;Fairtrade foundation.;The foundation was set up to certify different parts of the supply chain for many different global commodities. You’ve probably seen the well know Fairtrade logo on many different products including bananas, chocolate, sugar and coffee.;
Also Check: Will Coffee Help Me Lose Weight
Benefits On The Workers
As mentioned earlier, Fairtrade standards protects farmers and ensures that they are paid and treated fairly, regardless of what the market price is. Other benefits include safe working conditions, no discrimination, no forced/child labour, no harmful chemical use and health care/leave benefits being met or exceeded.
Fairtrade farmers and workers are also able to invest their Fairtrade premiums in social and business development projects, such as scholarship programs, healthcare services and quality improvement training to care for the land and the environment.
Does Fair Trade Actually Help Farmers Though
In a 2011 deep dive on the impact of fair trade on the coffee industry in particular published by Stanford Social Innovation Review, economist Colleen Haight submits that fair trade’s greatest success, arguably, is the increased consumer awareness surrounding some of the exploitative practices used against impoverished coffee farmers. But as far as bringing poverty relief to farmers overall, Haight argues that FLO and Fair Trade USA’s models have left a lot to be desired.
For example, the floor price can in practice become a price ceiling for some farmers during a bumper crop year. If the price of coffee falls to $1.00 per pound because there’s been a plentiful harvest in numerous countries, for example, then some fair trade buyers won’t pay more than $1.20 regardless of the quality of the seller’s beans. This leaves farmers with less incentive to participate in the fair trade system or to improve their growing methods. This also means that fair trade coffee is often subpar in quality compared to premium coffees that don’t bear fair trade certification. Farmers will save their best beans for buyers who will pay above market price rather than settle for fair trade buyers who will only meet the bare minimum.;
You May Like: Diet Snapple Raspberry Tea Caffeine
Fair Trade Harms Other Farmers
Overproduction argument
Critics argue that fair trade harms all non-Fairtrade farmers. Fair trade claims that its farmers are paid higher prices and are given special advice on increasing yields and quality. Economists state that, if this is indeed so, Fairtrade farmers will increase production. As the demand for coffee is highly elastic, a small increase in supply means a large fall in market price, so perhaps a million Fairtrade farmers get a higher price and 24 million others get a substantially lower price. Critics quote the example of farmers in Vietnam being paid over the world price in the 1980s, planting much coffee, then flooding the world market in the 1990s. The fair trade minimum price means that when the world market price collapses, it is the non-fair trade farmers, particularly the poorest, who have to cut down their coffee trees. This argument is supported by mainstream economists, not just free marketers.
The Purpose Of The Fair Trade Producer Standards
Fair Trade USA’s standards are designed to protect global workers and the environment. The organization regularly reviews standards to ensure they’re providing maximum value to producers and workers while still remaining practical for businesses. These standards encompass sustainable prices and wages, safe working conditions, biodiversity, and sustainable production, as well as how the Fair Trade Premium is allocated to improve farms, factories, fisheries, and businesses.
More information for each of the categories is available on Fair Trade USA’s website.;
Don’t Miss: Is There Caffeine In Snapple
Fairtrade Or Fair Tradeyes There Is A Slight Difference
Not to be confused with free trade , this is a certification formally introduced in 1997 by an organization formerly known as Fairtrade Labeling Organizations International, or FLO, and now called simply Fairtrade International; it was inspired by a Dutch mark known as Max Havelaar, which was an early mark named for the eponymous character in a novel about exploitative Dutch practices in the coffee growing areas of the Indonesian colonies. The principles of the Max Havelaar mark, which were designed to prevent abuse and exploitation of laborers in coffee, inspired similar sorts of initiatives in Europe and the United States, and today, Fairtrade International certification is applied to products across myriad industries, from coffee and chocolate to flowers, bananas, honey, cotton, and more, and includes organizations in Africa, Asia, and Mesoamerica.
The TL;DR here is that whether your coffee is Fair Trade- or Fairtrade-certified, there is a premium attached to it that is designed to incentivize producers to do good and responsible work, to make efficient and beneficial decisions about pooling or acquiring resources, and to offer some degree of price stability in volatile economic times.
Organizations Promoting Fair Trade
Most of the fair trade import organizations are members of, or certified by one of several national or international federations. These federations coordinate, promote, and facilitate the work of fair trade organizations. The following are some of the largest:
In 1998, the first four federations listed above joined together as FINE, an informal association whose goal is to harmonize fair trade standards and guidelines, increase the quality and efficiency of fair trade monitoring systems, and advocate fair trade politically.
- Additional certifiers include IMO , Eco-Social and Fair Trade USA.
- The Fair Trade Federation , created in 1994, is an association of Canadian and American fair trade wholesalers, importers, and retailers. The organization links its members to fair trade producer groups while acting as a clearinghouse for information on fair trade and providing resources and networking opportunities to its members. Members self-certify adherence to defined fair trade principles for 100% of their purchasing/business. Those who sell products certifiable by Fairtrade International must be 100% certified by FI to join FTF.
Student groups have also been increasingly active in the past years promoting fair trade products. Although hundreds of independent student organizations are active worldwide, most groups in North America are either affiliated with United Students for Fair Trade , or Fair Trade Campaigns , which also houses Fair Trade Universities and Fair Trade Schools.
Also Check: Is There Caffeine In Snapple
What Are Requirements For Businesses
As part of this agreement, buyer companies pay a minimum price for the coffee beans. This minimum price allows for some stability for farmers growing a commodity with world prices that can be highly volatile. In addition to this minimum price, coffee farmers are paid a premium. They use this premium to invest in their business, environmental sustainability, and their communities. Certifying organizations such as Fairtrade International set minimum prices and premiums.
Businesses who want to use the Fairtrade label on their coffee products must apply for a license from the organization to do so. Besides coffee, fair trade products include sugar, cocoa, bananas, and cotton, among many other food and non-food products. However, fair trade is most well-established with coffee. It is a highly traded commodity in producing countries. In addition, the need for fair trade among coffee farmers is great. They tend to be smaller producers who would have less clout in establishing prices.
Large Companies And Commodities
Large transnational companies have begun to use fair trade commodities in their products. In April 2000, Starbucks began offering fair trade coffee in all of their stores. In 2005, the company promised to purchase ten million pounds of fair trade coffee over the next 18 months. This would account for a quarter of the fair trade coffee purchases in the United States and 3% of Starbucks’ total coffee purchases. The company maintains that increasing its fair trade purchases would require an unprofitable reconstruction of the supply chain. Fair trade activists have made gains with other companies: Sara Lee Corporation in 2002 and Procter & Gamble in 2003 agreed to begin selling a small amount of fair trade coffee. , the world’s biggest coffee trader, began selling a blend of fair trade coffee in 2005. In 2006, The Hershey Company acquired Dagoba, an organic and fair trade chocolate brand.
Much contention surrounds the issue of fair trade products becoming a part of large companies. Starbucks is still only 3% fair trade â enough to appease consumers, but not enough to make a real difference to small farmers, according to some activists. The ethics of buying fair trade from a company that is not committed to the cause are questionable; these products are only making a small dent in a big company even though these companies’ products account for a significant portion of global fair trade.
| Business type |
|---|
Also Check: Caramel Ribbon Crunch Frappuccino Venti Price
What Is Fairtrade Coffee
Fairtrade was born in response to struggling Mexican coffee farmers and the collapse of world coffee prices in 1988. Basically, Fairtrade creates a fair and sustainable way for coffee farmers to trade and ensures that these farmers earn a higher minimum wage, even if the market price drops.
Everyone in the supply chain benefits from Fairtrade practices. Farmers are able to live a sustainable lifestyle, brands can offer quality products and consumers can put trust into the brands that they purchase its a win-win for everyone!
Is Fair Trade Coffee Organic
Fair Trade coffee is not organic by policy, but they encourage environmentally sustainable practices for coffee growers. USDA Organic certification includes its own set of qualifications about the growing, fertilization, and pest control practices used by coffee growers. See this list for some of the best sustainable coffee brands.
Also Check: Is There Caffeine In Snapple
How Does Fair Trade Work A Summary
Today, there are over 1.6 million people involved in fair trade certified organizations and schemes in 73 different countries in the world. The fair trade model has evolved from early examples of buying from small-scale sellers on low incomes to creating an expansive network that provides opportunities for growers, farmers, and producers in every corner of the globe.
The concept of fair trade rewards people based on the produce they sell, rather than their country of origin or their social or economic status. By creating a level playing field, smaller operations can compete with large-scale corporations, and workers and growers reap the rewards of higher prices and minimum fees. There are drawbacks and benefits of fair trade like everything in life, but in the vast majority of cases, the positives far outweigh the negatives.
Over the years, fair trade has really taken off, and ethical, sustainable products are more popular than ever before. Theres a much wider range of items available, and the industry has diversified. Coffee, tea, and chocolate have always been popular, but fair trade fashion and beauty are trends that are gathering pace. As time passes, and studies suggest that consumers are willing to pay more for certified products, it seems as though fair trade will continue to grow and flourish.
What The Heck Does Fair Trade Certified Mean
- Look for the Fair Trade Certified label on goods such as tea, cocoa, coffee and more.
You see it on labels for coffee, chocolate, flowers and more, but what does it really mean? Fair Trade is a designation developed to help consumers support products that come from farms that have been certified to provide fair wages and safe working conditions .;In addition, producers on certified farms are paid a premium to apply to projects such as healthcare, womens leadership initiatives and micro-finance programs, as voted on by the farmers and workers themselves.
Fair Trade Certified also ensures that farmers obey internationally monitored environmental standards, while empowering farmers and farm workers with financial incentives and resources for organic conversion, reforestation, water conservation and environmental education.
Goods that bear the;Fair Trade Certified label carry an independent, third-party-verified guarantee that the farmer received a fair price for the crop, and is empowered to compete in the global marketplace through direct, long-term contracts with international buyers. This market access lifts farming families from poverty through trade not aid which keeps food on the table, children in school and families on their land.;
fair trade means the legal trade of contents from all around the world for the reasonable price
If you know this for a fact, you must be dead too.
Recommended Reading: Is Coffee Good For Constipation
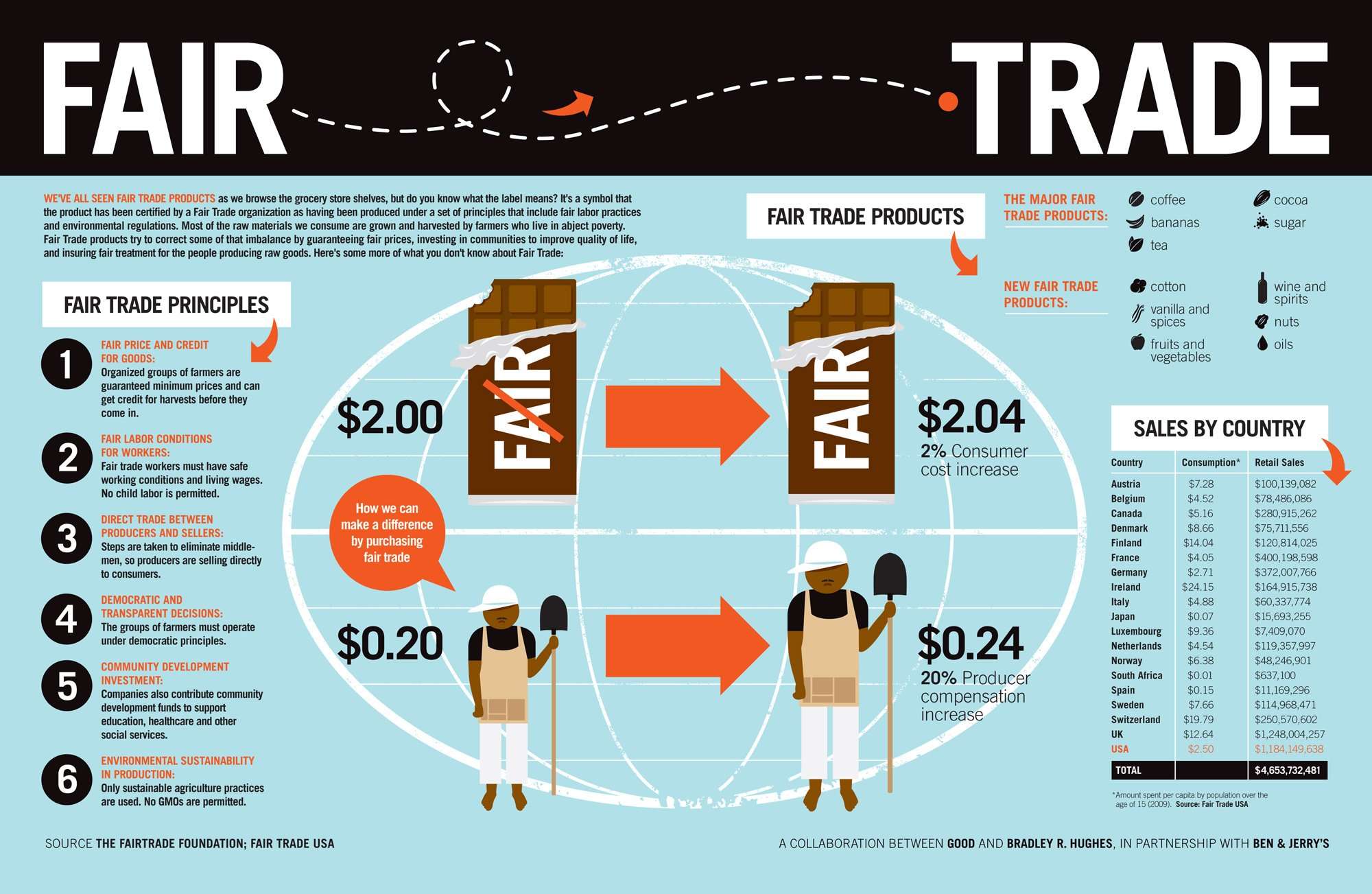
Principles Of Fair Trade
The goal of Fair Trade is to reduce poverty for farmers and workers in developing countries. This means not just paying them more in the short term, but also helping them improve their skills, build up their;communities, and protect the local environment so its resources will be there for future generations.
Organizations involved in Fair Trade, including Fair Trade USA and the Fair Trade Federation, have outlined several;basic principles for both buyers and sellers to follow:
1. Direct TradeFair Trade importers work with producers as directly as possible. Cutting out the middleman enables the importers to pay the farmers a larger share of the money their products will eventually fetch on store shelves. Fair Trade importers often deal with;collectives ;groups of small-scale growers who run their own farms with little or no hired labor. To meet Fair Trade standards, the collectives must be democratically run, with each farmer;getting a vote, and must split their profits equally among all the members.
2. Fair PriceFair Trade guarantees farmers a reasonable minimum price for their crops, no matter how low the market price falls. Buyers promise to;pay producers promptly for their goods, and producers promise in turn to pay a fair wage to all their;workers. Buyers also extend credit to their producers for instance, paying them in advance of the harvest to make sure the producers have all the resources they need to turn over their goods on time.
Direct Trade Vs Fair Trade
Direct trade is a phrase used to describe coffee buying that involves some sort for of direct connection with coffee producers. Usually, it means that an importer is working directly with producers aiming to pay more than the Fair Trade base price. Many of the coffees we source fall under this category. For example, our;Relationship Coffees;are perfect examples of coffees bought through our direct links with producers. Our Costa Rican coffees have been purchased at more than double the Fairtrade price from small producers who are independent and not fully associated with a co-operative. The coffees we buy from Rwanda do come from large co-operative organizations. Bwishaza is Fairtrade certified while Liza washing station is not. We pay the same price to both producers with the washed coffees earning them 1.45x and natural processed coffees 2.28x the Fairtrade minimum price.
Also Check: Can You Drink Coffee After Wisdom Teeth Removal